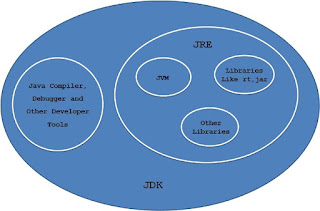
What are JDK, JRE and JVM?
JDK,
JRE and JVM
JDK,
JRE and JVM are most
commonly heard in the Java programming language.
Many
people get confused with these 3 terms or they think that they are one and the
same, unfortunately they are not synonyms, and each one has got its own
responsibility.
What is JVM?
1. It
stands for Java Virtual Machine
2. JVM is
responsible for converting byte code into machine specific code because of which we have different
JVM for different
Operating system, like different JVM for Windows, Linux or Solaris.
3. But
all the JVMs understand the byte
code given to it no
matter from which machine the byte code got created. This makes Java
platform independent.
4. The Java Virtual machine (JVM)
is the virtual machine that runs the Java bytecodes. The JVM doesn't understand
Java source code, that's why you compile your
*.java files to obtain *.class files
that contain the bytecodes understandable by the JVM. It's also the entity that
allows Java to be a "portable language" (write once, run anywhere). Indeed
there are specific implementations of the JVM for different systems (Windows,
Linux, MacOS).
5. As
we all aware when we compile a Java file, output is not an ‘exe’ but it’s a
‘.class’ file. ‘.class’ file consists of Java byte codes which are
understandable by JVM. Java Virtual Machine interprets the byte code into the
machine code depending upon the underlying operating system and hardware
combination. It is responsible for all the things like garbage collection,
array bounds checking, etc… JVM is platform dependent.
6.
JVM also provides several paramount features including Memory
Management, Garbage Collection and
Security etc.
7. We
can customize the JVM by using Java options.
8. We
can allocate maximum and minimum memory for Heap residing in JVM.
9. JVM
is Virtual because it does
not exist physically; we
can’t install JVM as it comes with JRE.
10. The JVM is
called “virtual” because it provides a machine interface that does not depend
on the underlying operating system and machine hardware architecture. This
independence from hardware and operating system is a cornerstone of the
write-once run-anywhere value of Java programs.
11. There
are different JVM implementations are there. These may differ in things like
performance, reliability, speed, etc. These implementations will differ in those
areas where Java specification doesn’t mention how to implement the features,
like how the garbage collection process works is JVM dependent, Java spec
doesn’t define any specific way to do this.
12. The JVM performs following main
tasks:
o
Loads code
o
Verifies code
o
Executes code
o
Provides runtime environment
What is JRE?
1. It
stands for Java Runtime Environment
2. It
is the implementation of JVM, it physically
exists, and hence we can install JRE.
3. It
provides the platform to execute/run the java programs.
4. It
consists of JVM and
other libraries like rt.jar which are required to execute the Java
program.
5. We
can run any Java program using JRE but we can’t compile the java code using JRE as it does not
contain any compiler, debugger etc.
6. We
can see JRE installed in many places like Broswers,
TV, Mobile, set-top boxes and
most of the electronic gadgets.
7. JRE
in these places uses the JVM and executes the byte code provides in the form of JAR.
8. JRE = JVM + Required Library to run Application
9. The
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) provides the libraries, the Java Virtual
Machine, and other components to run applets and applications written in the
Java programming language. In addition, two key deployment technologies are
part of the JRE: Java Plug-in, which enables applets to run in popular
browsers; and Java Web Start, which deploys standalone applications over a
network. It is also the foundation for the technologies in the Java 2 Platform,
Enterprise Edition (J2EE) for enterprise software development and deployment.
The JRE does not contain tools and utilities such as compilers or debuggers for
developing applets and applications.
10. Java
Runtime Environment contains JVM, class libraries, and other supporting files.
It does not contain any development tools such as compiler, debugger, etc.
Actually JVM runs the program, and it uses the class libraries, and other
supporting files provided in JRE. If you want to run any java program, you need
to have JRE installed in the system
11. The
Java Virtual Machine provides a platform-independent way of executing code; that
mean compile once in any machine and run it anywhere (any machine).
What is JDK?
1. It
stands for Java Development Kit and it physically
exists and we can
install it.
2. It
contains JRE + Development tools like compiler, debugger etc.
3. Since
it contains JRE along
with compiler,
we can write java code and compile the java code.
4. Similar
to JRE, JDK is also platform specific, we need to use
separate JDK for different
Operating system like
Windows, Linux etc.
5. All
the libraries like Java, Javac etc exist inside the bin
folder of JDK installed
path.
6. The
JDK is a superset of the JRE, and contains everything that is in the JRE, plus
tools such as the compilers and debuggers necessary for developing applets and
applications.
7. Java
Developer Kit contains tools needed to develop the Java programs, and JRE to
run the programs. The tools include compiler (javac.exe), Java application
launcher (java.exe), Appletviewer, etc…
8.
Compiler converts java code into byte code. Java
application launcher opens a JRE, loads the class, and invokes its main method.
9.
You need JDK, if at all you want to write your own
programs, and to compile them. For running java programs, JRE is sufficient.
10. JRE
is targeted for execution of Java files
11. i.e. JRE
= JVM + Java Packages Classes (like util, math, lang, awt,swing etc)+runtime
libraries.
12. JDK
is mainly targeted for java development. You can create a Java file (with the
help of Java packages), compile a Java file and run a java file.
Difference between JDK, JRE and
JVM
·
JDK is a
super set of JRE which
contains the JRE along with compiler; hence it can be used for development purposes.
·
JRE contains JVM and other run
time libraries required
to execute the program.
·
It does not contain other development
tools like compiler,
debugger etc.
·
Hence we can install JRE only to run
the Java applications not to develop them.
·
JVM cannot be installed as it does
not have any physical
existence.
·
It comes with JRE and JDK installation.
·
It provides platform independence by converting the bytecode obtained from any machine into
corresponding machine instructions but it is created only when we execute
the java program.
What is JIT Compiler?
1. It
stands for Just In Time Compiler, it was
introduced to improve the performance of Java Virtual machine.
2. As
we know JVM converts the bytes
code into machine
instructions, JIT helps
to improve this operation by converting similar
byte codes into machine
instruction at the same
time.
3. Hence
it reduces the overall execution time of program.
4. JIT is
also a part of JVM.
The below chart shows the different features of each of the
Java technologies.




Comments
Post a Comment