Android Interview Questions - Fresher
Android Interview Questions -Fresher
What
is Android?
Android
is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system,
middleware and key applications.
What are the
features of Android?
1. SQLite
enables to store the data in a structured manner.
2. Supports
GSM telephone and Bluetooth, WiFi, 3G and EDGE technologies
3. The
development is a combination of a device emulator, debugging tools, memory
profiling and plug-in for Eclipse IDE.
4. Components
can be reused and replaced by the application framework.
5. Optimized
DVM for mobile devices
Describe
the APK format.
The APK file is
compressed the AndroidManifest.xml file, application code (.dex files),
resource files, and other files. A project is compiled into a single .apk file.
What
is an action?
A description of
something that an Intent sender desires.
What is an activity?
A single screen in an application, with supporting Java code.
An activity presents a visual user interface for one focused
endeavor the user can undertake.
For example, an activity might present a list of menu items
users can choose from or it might display photographs along with their
captions.
What
is a service?
Service is log
running operation in background.
For example, a
service might play background music as the user attends to other matters, or it
might fetch data over the network or calculate.
What is a Broadcast receiver?
A broadcast
receiver is a component that does nothing but receive and react to broadcast
announcements.
For example,
announcements that the timezone has changed, that the battery is low or that
the user changed a language preference
What
is a content provider?
A content provider
makes a specific set of the application’s data available to other applications.
The content provider extends the ContentProvider base class to implement a
standard set of methods that enable other applications to retrieve and store
data of the type it controls.
However,
applications do not call these methods directly. Rather they use a
ContentResolver object and call its methods instead.
What
is intent?
A class (Intent)
describes what a caller desires to do. The caller sends this intent to
Android’s intent resolver, which finds the most suitable activity for the
intent.
How
is nine-patch image different from a regular bitmap?
It is a resizable
bitmap resource that can be used for backgrounds or other images on the device.
The NinePatch class permits drawing a bitmap in nine sections. The four corners
are unscaled; the four edges are scaled in one axis, and the middle is scaled
in both axes.
Which
language does Android support for application development?
Android
applications are written using the Java programming language.
What
is a resource?
A user-supplied
XML, bitmap, or other file, injected into the application builds process, which
can later be loaded from code.
How can we write code for Android using
C/C++?
Yes, but need to use NDK
Android applications are written using the Java
programming language. Android includes a set of core libraries that provides
most of the functionality available in the core libraries of the Java
programming language.
Every Android application runs in its own process,
with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine. Dalvik has been written so
that a device can run multiple VMs efficiently. The Dalvik VM executes files in
the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format which is optimized for minimal memory
footprint. The VM is register-based, and runs classes compiled by a Java
language compiler that have been transformed into the .dex format by the
included “dx” tool.
Android only supports applications written using the Java programming language at this time.
Android only supports applications written using the Java programming language at this time.
What is manifest file?
An XML file associated with each Application that
describes the various activities, intent filters, services, and other items
that it exposes.
Which dialog boxes are supported in android?
Android supports 4 dialog boxes:
1. AlertDialog: An alert dialog box supports 0 to 3 buttons and a list
of selectable elements, including check boxes and radio buttons. Among the
other dialog boxes, the most suggested dialog box is the alert dialog box.
2. ProgressDialog: This dialog box displays a progress wheel or a progress
bar. It is an extension of AlertDialog and supports adding buttons.
3. DatePickerDialog: This dialog box is used for selecting a date by the
user.
4. TimePickerDialog: This dialog box is used for selecting time by the user.
What does “compatibility” mean?
We define an “Android compatible” device as one that can run any
application written by third-party developers using the Android SDK and NDK. We
use this as a filter to separate devices that can participate in the Android
app ecosystem, and those that cannot. Devices that are properly compatible can
seek approval to use the Android trademark. Devices that are not compatible are
merely derived from the Android source code and may not use the Android
trademark.
In other words, compatibility is a prerequisite to participate
in the Android apps ecosystem. Anyone is welcome to use the Android source
code, but if the device isn’t compatible, it’s not considered part of the
Android ecosystem.
What is the role of Android Market in compatibility?
Devices that are Android compatible may seek to license the
Android Market client software. This allows them to become part of the Android
app ecosystem, by allowing users to download developers’ apps from a catalog
shared by all compatible devices. This option isn’t available to devices that
aren’t compatible.
What kinds of devices
can be Android compatible?
The Android software can be ported to a lot of different kinds
of devices, including some on which third-party apps won’t run properly. The
Android Compatibility Definition Document (CDD) spells out the specific device
configurations that will be considered compatible.
For example, though the Android source code could be ported to
run on a phone that doesn’t have a camera, the CDD requires that in order to be
compatible, all phones must have a camera. This allows developers to rely on a
consistent set of capabilities when writing their apps.
The CDD will evolve over time to reflect market realities. For
instance, the 1.6 CDD only allows cell phones, but the 2.1 CDD allows devices
to omit telephony hardware, allowing for non-phone devices such as tablet-style
music players to be compatible. As we make these changes, we will also augment
Android Market to allow developers to retain control over where their apps are
available. To continue the telephony example, an app that manages SMS text messages would
not be useful on a media player, so Android Market allows the developer to
restrict that app exclusively to phone devices.
If my device is compatible, does it automatically have access to
Android Market and branding?
Android Market is a service operated by Google. Achieving compatibility is a prerequisite for obtaining access to the Android Market software and branding. Device manufacturers should contact Google to obtain access to Android Market.
Android Market is a service operated by Google. Achieving compatibility is a prerequisite for obtaining access to the Android Market software and branding. Device manufacturers should contact Google to obtain access to Android Market.
How can I get access to the Google apps for Android, such as
Maps?
The Google apps for Android, such as YouTube, Google Maps and
Navigation, Gmail, and so on are Google properties that are not part of
Android, and are licensed separately. Contact android-partnerships@google.com
for inquiries related to those apps.
How to select more than one option from list in android xml
file? Give an example.
Specify android id, layout height and width as depicted in the
following example.
<ListView android:id="@+id/ListView01"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"> </ListView>
What is needed to make a multiple choice list with a custom view
for each row?
Multiple choice list can be viewed by making the CheckBox
android:id value be “@android:id /text1". That is the ID used by Android
for the CheckedTextView in simple_list_item_multiple_choice.
What is the TTL (Time to Live)? Why is it required?
TTL is a value in data packet of Internet Protocol. It
communicates to the network router whether or not the packet should be in the
network for too long or discarded. Usually, data packets might not be
transmitted to their intended destination within a stipulated period of time.
The TTL value is set by a system default value which is an 8-bit binary digit
field in the header of the packet. The purpose of TTL is, it would specify
certain time limit in seconds, for transmitting the packet header. When the
time is exhausted, the packet would be discarded. Each router receives the
subtracts count, when the packet is discarded, and when it becomes zero, the
router detects the discarded packets and sends a message, Internet Control
Message Protocol message back to the originating host.
What is Fragmentation?
Fragmentation is a process of breaking the IP packets into
smaller pieces. Fragmentation is needed when the datagram is larger than the
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit).Each fragment becomes a datagram in itself and
transmitted independently from source. When received by destination they are
reassembled.
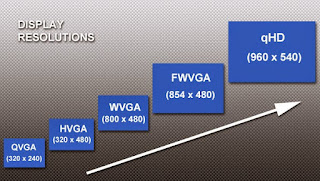
Difference between HVGA and Display QVGA in Android
QVGA or Quick
Video Graphics Adapter is a screen that has a resolution of 240 x 320 Pixel.
While HVGA or High Video Graphics Adapter is a screen that has a resolution of
320 x 480 px.
Well, from the size of the resolution HVGA screen size we can see if it is much larger than QVGA. Not only that, no matter if HVGA resolution is sharper at HVGA appeal. But besides that, phones with HVGA screens tend to be more wasteful of energy because of the huge resolution.
Well, from the size of the resolution HVGA screen size we can see if it is much larger than QVGA. Not only that, no matter if HVGA resolution is sharper at HVGA appeal. But besides that, phones with HVGA screens tend to be more wasteful of energy because of the huge resolution.
Differences in screen
resolution are also give impact on applications that can run, such as games. There
is a different kind of games for HVGA and QVGA screen. So if you want to
install games on android, make sure the games are compatible with its
resolution or not.
What is difference
between DOM and SAX parser?
DOM parser is an in
memory parser so it loads whole XML file in memory and create a DOM tree to parse.
SAX parser is an event based parser, so it parses XML document based upon event
received e.g. opening tag, closing tag, start of attribute or end of attribute.
Because of their working methodology, DOM parser is not suitable for large XML
file as they will take lot of space in memory and your process may ran out of
memory, SAX is the one which should be used to parse large files. For small
files, DOM is usually much faster than SAX.



Comments
Post a Comment