Stack and Queue Introduction
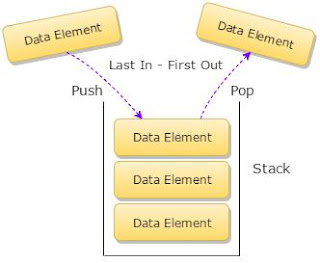
Stack A stack is a basic data structure that can be logically thought as linear structure represented by a real physical stack or pile, a structure where insertion and deletion of items takes place at one end called top of the stack. The basic concept can be illustrated by thinking of your data set as a stack of plates or books where you can only take the top item off the stack in order to remove things from it. This structure is used all throughout programming. The basic implementation of a stack is also called a LIFO (Last In First Out) to demonstrate the way it accesses data, since as we will see there are various variations of stack implementations. There are many real life examples of stack. Consider the simple example of plates stacked over one another in canteen. The plate which is at the top is the first one to be removed, i.e. the plate which has been placed at the bottommost position remains in the stack for the longest period of time. So, it can be simply seen to ...

