Java I/O Tutorial
Java I/O Tutorial
Java I/O (Input and Output)
is used to process the input and produce the output.
Java uses the concept of stream to make I/O operation fast. The
java.io package contains all the classes required for input and output
operations.
We can perform file handling in java by Java I/O
API.
Stream
A stream is a sequence of data. In Java a stream is composed of
bytes. It's called a stream because it is like a stream of water that continues
to flow.
In java, 3 streams are created for us automatically. All these
streams are attached with console.
1) System.out: standard output stream
2) System.in: standard input stream
3) System.err: standard error stream
Let's see the code to print output and error message
to the console.
System.out.println("simple message");
System.err.println("error message");
Let's see the code to get input from console.
int i=System.in.read(); //returns ASCII code of 1st character
System.out.println((char)i); //will print the character
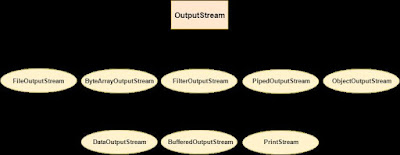
OutputStream
Java application uses an output stream to
write data to a destination, it may be a file, an array, peripheral device or
socket.
InputStream
Java application uses an input stream to
read data from a source, it may be a file, an array, peripheral device or
socket.
Let's understand working of Java
OutputStream and InputStream by the figure given below.
Java FileOutputStream
Example 1: write byte
import
java.io.FileOutputStream;
public
class FileOutputStreamExample {
public static void main(String
args[]){
try{
FileOutputStream fout=new
FileOutputStream("D:\\myfile.txt");
fout.write(65);
fout.close();
System.out.println("success...");
}catch(Exception
e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Java FileOutputStream
example 2: write string
import
java.io.FileOutputStream;
public
class FileOutputStreamExample {
public static void main(String
args[]){
try{
FileOutputStream fout=new
FileOutputStream("D:\\myfile.txt");
String s="Welcome to
Beautiful India";
byte b[]=s.getBytes();//converting
string into byte array
fout.write(b);
fout.close();
System.out.println("success...");
}catch(Exception
e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Java FileInputStream
example 1: read single character
import
java.io.FileInputStream;
public
class DataStreamExample {
public static void main(String
args[]){
try{
FileInputStream fin=new
FileInputStream("D:\\myfile.txt");
int i=fin.read();
System.out.print((char)i);
fin.close();
}catch(Exception
e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Java FileInputStream
example 2: read all characters
import
java.io.FileInputStream;
public
class DataStreamExample {
public static void main(String
args[]){
try{
FileInputStream fin=new
FileInputStream("D:\\myfile.txt");
int i=0;
while((i=fin.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)i);
}
fin.close();
}catch(Exception
e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Java
BufferedOutputStream Class
Java BufferedOutputStream class is used
for buffering an output stream. It internally uses buffer to store data. It
adds more efficiency than to write data directly into a stream. So, it makes
the performance fast.
For adding the buffer in an OutputStream,
use the BufferedOutputStream class.
Java
BufferedInputStream Class
Java BufferedInputStream
class is used to read information from stream. It internally uses buffer
mechanism to make the performance fast.
The important points
about BufferedInputStream are:
- When the bytes from the stream
are skipped or read, the internal buffer automatically refilled from the
contained input stream, many bytes at a time.
- When a BufferedInputStream is
created, an internal buffer array is created.
Java DataOutputStream
Class
Java DataOutputStream class allows an
application to write primitive Java data types to the output stream in a
machine-independent way.
Java application generally uses the data
output stream to write data that can later be read by a data input stream.
Java DataInputStream
Class
Java DataInputStream class allows an
application to read primitive data from the input stream in a
machine-independent way.
Java application generally uses the data
output stream to write data that can later be read by a data input stream.
Java FileWriter Class
Java FileWriter class is used to write
character-oriented data to a file. It is character-oriented class which is used
for file handling in java.
Unlike FileOutputStream class, you don't
need to convert string into byte array because it provides method to write
string directly.
Java FileReader Class
Java FileReader class is used to read data
from the file. It returns data in byte format like FileInputStream class.
It is character-oriented class which is
used for file handling in java.
Java BufferedWriter
Class
Java BufferedWriter class is used to
provide buffering for Writer instances. It makes the performance fast. It
inherits Writer class. The buffering characters are used for providing the
efficient writing of single arrays, characters, and strings.
Java BufferedReader
Class
Java BufferedReader class is used to read
the text from a character-based input stream. It can be used to read data line
by line by readLine() method. It makes the performance fast. It inherits Reader
class.
Reading data from
console by InputStreamReader and BufferedReader
In this example, we are connecting the
BufferedReader stream with the InputStreamReader stream for reading the line by
line data from the keyboard.
import
java.io.*;
public
class BufferedReaderExample{
public
static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
InputStreamReader r=new
InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br=new
BufferedReader(r);
System.out.println("Enter your
name");
String name=br.readLine();
System.out.println("Welcome
"+name);
}
}
Java StringTokenizer
In Java, you can StringTokennizer class to
split a String into different tokenas by defined delimiter. (space is the
default delimiter).
Uses StringTokennizer to split a string by “space” and “comma” delimiter, and
iterate the StringTokenizer elements and print it out one by one.
import
java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class App
{
public static void main(String[]
args) {
StringTokenizer st = new
StringTokenizer("my name is piyush");
while
(st.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
}
String
str = "This is String, split by StringTokenizer, created by Piyush";
st = new
StringTokenizer(str);
System.out.println("----
Split by space ------");
while
(st.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(st.nextElement());
}
System.out.println("----
Split by comma ',' ------");
StringTokenizer st2 =
new StringTokenizer(str, ",");
while
(st2.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(st2.nextElement());
}
}
}







Comments
Post a Comment